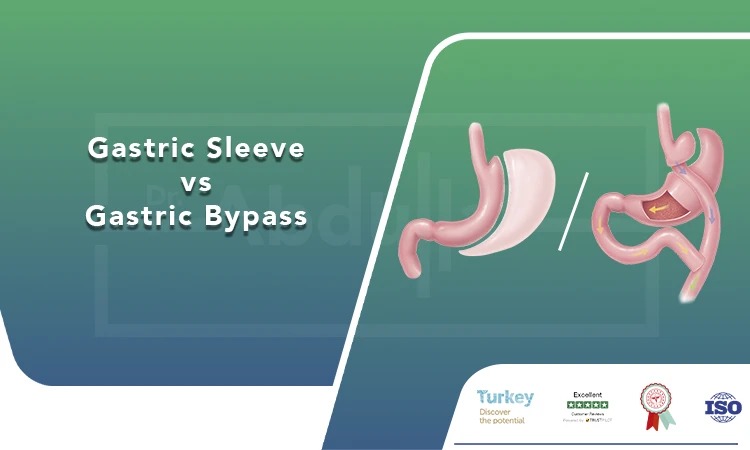
Gastric sleeve vs gastric bypass is a common comparison for those considering bariatric surgery. Both procedures are designed to promote weight loss by reducing stomach size and limiting food intake, but they work in different ways. Gastric sleeve surgery involves removing a portion of the stomach to create a smaller, tube-like structure, while gastric bypass reroutes the digestive system to bypass part of the stomach and small intestine. Each procedure has its benefits and risks, making the choice highly dependent on an individual’s health condition, weight loss goals, and lifestyle. Studies show that both surgeries lead to significant weight loss, with gastric bypass often resulting in slightly higher long-term success rates. However, gastric sleeve is generally simpler and has fewer complications, making it a preferred option for many patients.

What is Gastric Sleeve?
Gastric sleeve surgery, also known as sleeve gastrectomy, is a restrictive weight loss procedure where about 75-80% of the stomach is removed. This results in a smaller stomach that holds less food and reduces hunger hormones such as ghrelin, leading to lower appetite and calorie intake.
- Procedure: Laparoscopic removal of a large portion of the stomach.
- Weight Loss: Patients typically lose 60-70% of their excess weight within the first year.
- Recovery Time: Around 2-4 weeks.
- Complications: Lower risk than gastric bypass but may include acid reflux and nutrient deficiencies.
What is Gastric Bypass?
Gastric bypass, or Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB), is a combination of restrictive and malabsorptive procedures. The stomach is divided into a small pouch, and part of the small intestine is bypassed to reduce calorie absorption.
- Procedure: Stomach is divided, and the small intestine is rerouted.
- Weight Loss: More rapid and significant, with 70-80% excess weight loss in the first 12-18 months.
- Recovery Time: Typically 3-5 weeks.
- Complications: Higher risk than gastric sleeve, including dumping syndrome, nutritional deficiencies, and intestinal obstruction.
Which is Better? Sleeve or Bypass?
The choice depends on several factors:
- If simplicity and lower risk are priorities, gastric sleeve is better.
- If maximum weight loss and diabetes resolution are the main goals, gastric bypass may be preferable.
- Patients with severe acid reflux may benefit more from gastric bypass, as gastric sleeve can worsen symptoms.
Gastric Sleeve Pros and Cons
Pros
- Less invasive than gastric bypass.
- Lower risk of long-term complications.
- No intestinal rerouting means lower malabsorption issues.
- Shorter surgery time and quicker recovery.
- Effective weight loss, with 60-70% excess weight loss in the first year.
Cons
- Irreversible – once the stomach is removed, it cannot be restored.
- Can cause acid reflux.
- Slightly lower overall weight loss compared to gastric bypass.
Gastric Bypass Pros and Cons
Pros
- More significant and faster weight loss.
- Higher success rate in resolving type 2 diabetes.
- Reduces acid reflux, making it better for GERD patients.
Cons
- More complex surgery with higher risk of complications.
- Dumping syndrome can occur, causing nausea, dizziness, and diarrhea.
- Greater risk of nutritional deficiencies requiring lifelong supplementation.
Similarities of Gastric Sleeve and Gastric Bypass
- Both procedures help with significant weight loss.
- Both require permanent lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise.
- Patients must take vitamins and monitor nutrition after surgery.
- Each has a high success rate in treating obesity-related conditions like diabetes and sleep apnea.
Which One Is Simpler?
Gastric sleeve is simpler and less invasive, making it the preferred option for patients looking for a quicker recovery and lower risk of complications.
In conclusion, gastric sleeve is often the preferred choice for those seeking a less invasive, lower-risk procedure with effective weight loss results. However, gastric bypass remains a powerful option for those needing maximum weight loss and diabetes resolution. Consultation with a bariatric specialist is essential to determine the best choice based on individual health needs and goals.
Frequantly Asked Questions
Gastric bypass restricts food intake more significantly, so patients generally eat less than those with gastric sleeve.
Most patients maintain 50-60% of their excess weight loss, but some may experience weight regain if dietary guidelines are not followed.
Gastric sleeve is generally considered the safest option due to its lower complication rate compared to gastric bypass.
While most patients are satisfied, some regret the procedure due to acid reflux or inadequate weight loss compared to their expectations.